|
I am a Senior Vision Algorithm Expert at OnTIME, which is a Smart Mobility Platform under GAC Group. My work primarily involves the intersection of Computer Vision and Efficient Deep Learning. I receieved my master's degree from the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences. My master's years was spent in the Institute of Computing Technology and Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology of Chinese Academy of Sciences, under the supervision of Prof. Jianbin Jiao, Yu Qiao and Feng Dai. Email: yh.peng.tu@gmail.com |

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
  |
Peng Tu, Yawen Huang, Huimin Huang, Yefeng Zheng arxiv, in processing, 2023 Region-based deep neural networks have shown outstanding performances for object detection. These detectors typically consist of separate branches for classification and localization with shared features and multi-task loss functions, resulting in cumulative errors and thus affecting detection power. In this paper, we present a novel approach, Triplet ROI Alignment (TRIAL), which addresses the issue of false positive boxes in object detection. False positives, as the key factor, usually bring unfavorable impact causing degraded performances. The proposed TRIAL deals with this problem by directly suppressing the feature activation in these regions with three key procedures: 1) re-matching predictions into positive and negative boxes; 2) constructing triplet embeddings; 3) comparing positive and negative pairs in each triplet to guide detectors in generating more accurate and discriminative local visual features. TRIAL is user-friendly and can be integrated with any efficient and two-stage detectors, including YOLOX, YOLOF, and FasterRCNN. Extensive experiments demonstrate that TRIAL can significantly improve the mean average precision (mAP) of detectors by approximately 4$\%$ on the challenging COCO benchmark with reduced false positive samples. |
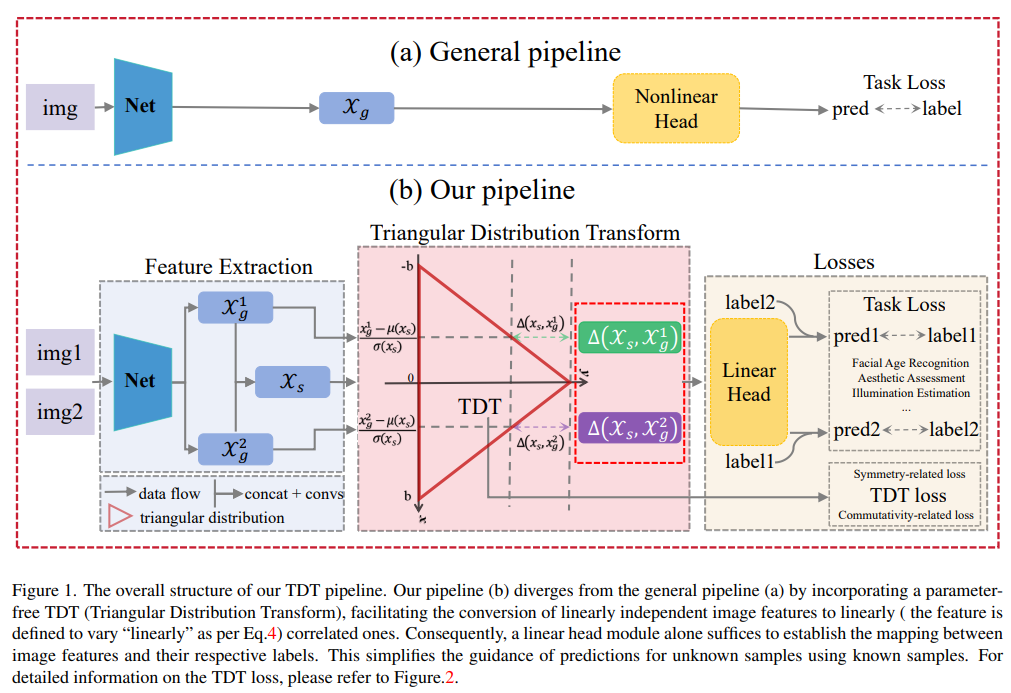  |
Ping Chen, Xingpeng Zhang, Chengtao Zhou, Dichao Fan, Peng Tu, Le Zhang, Yanlin Qian Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2024 Convolution neural network is successful in pervasive vision tasks, including label distribution learning, which usually takes the form of learning an injection from the nonlinear visual features to the well-defined labels. However, how the discrepancy between features is mapped to the label discrepancy is ambient, and its correctness is not guaranteed. To address these problems, we study the mathematical connection between feature and its label, presenting a general and simple framework for label distribution learning. We propose a so-called Triangular Distribution Transform (TDT) to build an injective function between feature and label, guaranteeing that any symmetric feature discrepancy linearly reflects the difference between labels. The proposed TDT can be used as a plug-in in mainstream backbone networks to address different label distribution learning tasks. Experiments on Facial Age Recognition, Illumination Chromaticity Estimation, and Aesthetics assessment show that TDT achieves on-par or better results than the prior arts. |
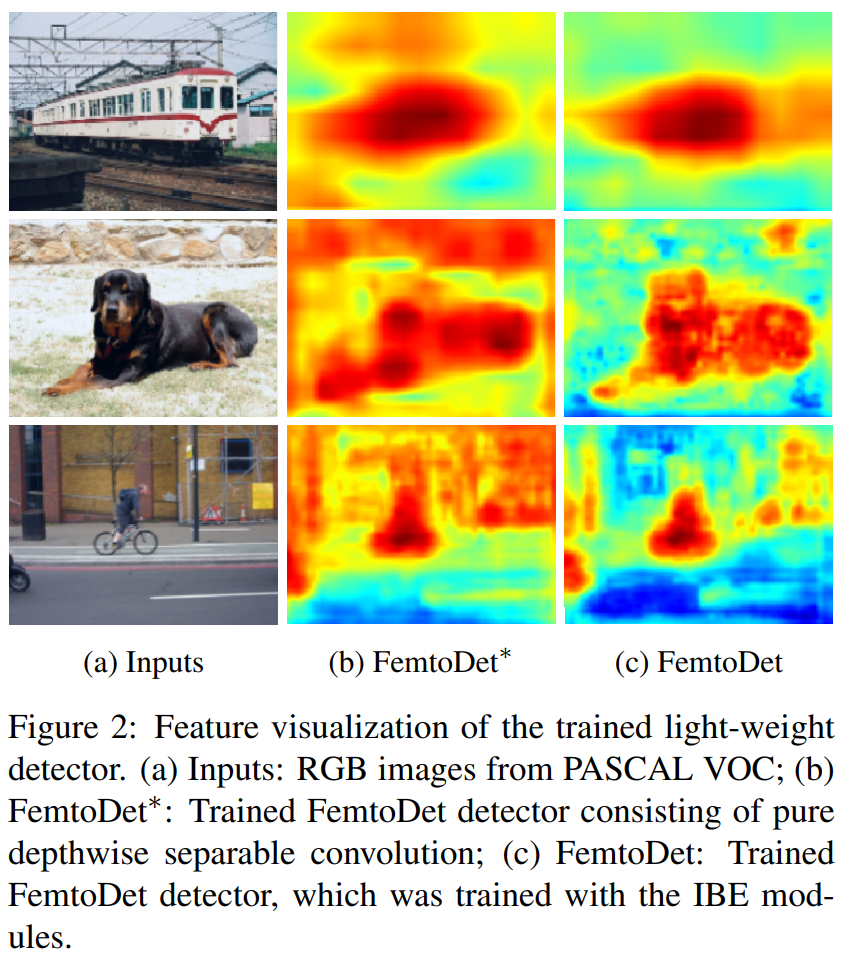  |
Peng Tu, Xu Xie, Guo AI, Yuexiang Li, Yawen Huang, Yefeng Zheng International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2023 Efficient detectors for edge devices are often optimized for parameters or speed count metrics, which remain in weak correlation with the energy of detectors. However, some vision applications of convolutional neural networks, such as always-on surveillance cameras, are critical for energy constraints. This paper aims to serve as a baseline by designing detectors to reach tradeoffs between energy and performance from two perspectives: 1) We extensively analyze various CNNs to identify low-energy architectures, including selecting activation functions, convolutions operators, and feature fusion structures on necks. These underappreciated details in past work seriously affect the energy consumption of detectors; 2) To break through the dilemmatic energy-performance problem, we propose a balanced detector driven by energy using discovered low-energy components named FemtoDet. In addition to the novel construction, we improve FemtoDet by considering convolutions and training strategy optimizations. Specifically, we develop a new instance boundary enhancement (IBE) module for convolution optimization to overcome the contradiction between the limited capacity of CNNs and detection tasks in diverse spatial representations, and propose a recursive warm-restart (RecWR) for optimizing training strategy to escape the sub-optimization of light-weight detectors by considering the data shift produced in popular augmentations. As a result, FemtoDet with only 68.77k parameters achieves a competitive score of 46.3 AP50 on PASCAL VOC and 1.11 W & 64.47 FPS on Qualcomm Snapdragon 865 CPU platforms. Extensive experiments on COCO and TJUDHD datasets indicate that the proposed method achieves competitive results in diverse scenes |
|
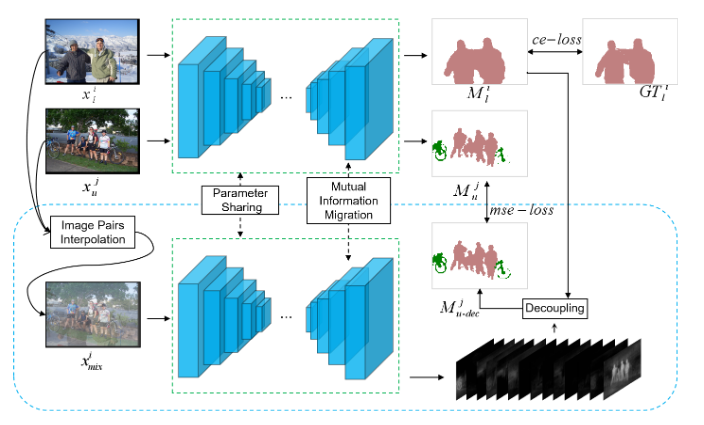
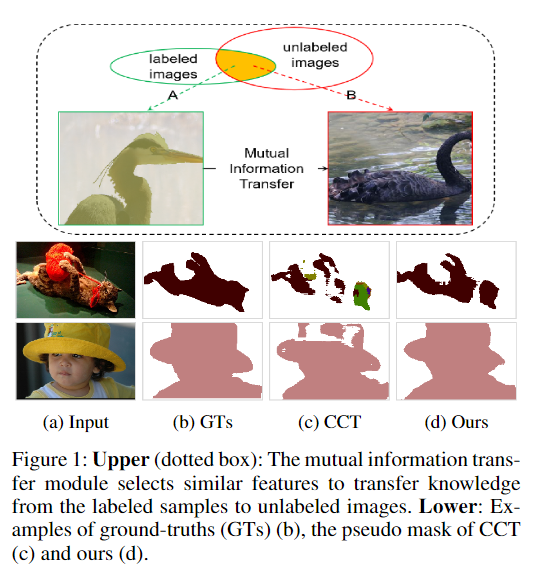
Peng Tu, Yawen Huang, Feng Zheng, Zhenyu He, Liujun Cao, Ling Shao Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), 2022 Semi-supervised learning is a challenging problem which aims to construct a model by learning from limited labeled examples. Numerous methods for this by treating labeled and unlabeled data separately often lead to discarding mass prior knowledge learned from the labeled examples. We propose a semi-supervised semantic segmentation method named GudedMix-Net, which leverages labeled information to guide the learning of unlabeled instances. Extensive experiments show that GuidedMix-Net significantly improves the mIoU by +7% compared to previous approaches. |
|
Website template borrowed from here. |